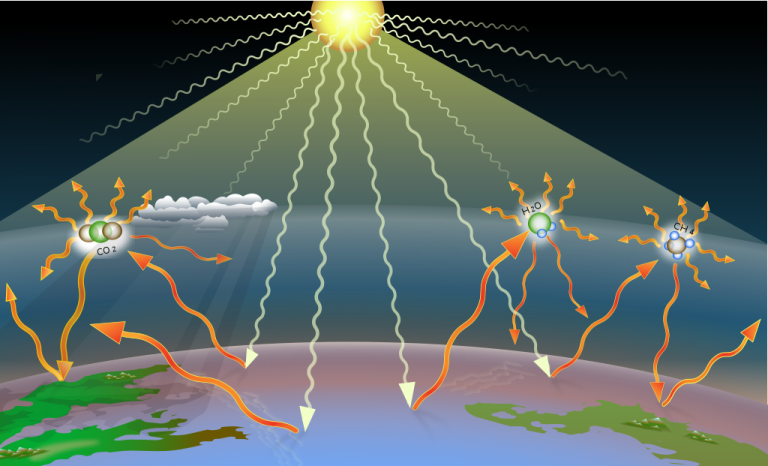
Or: How does carbon dioxide (CO2) trap heat in our atmosphere?
Where does CO2 come from? Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a natural gas that occurs in the Earth’s atmosphere, but ever since the discovery of fossil fuels the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere has been rapidly increasing. The primary sources of CO2 emissions are:
Power generation industry (gas & oil power stations) + fossil fuel exploitation + transportation (cars & road transport) + industrial processes + emissions from buildings and homes. [Click HERE for more information on global CO2 emissions].
You’ve probably already read that carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases act like a blanket or a cap, trapping some of the heat that Earth might have otherwise radiated out into space. That’s the simple answer. But how exactly do certain molecules trap heat? The answer there requires diving into physics and chemistry. Read more in this article by The Columbia Climate School – part of Columbia University, New York City, USA
What happens when we have too much CO2? Here is a short video by Joe Collins (@loveandrespect85 ) explaining the phenomenon.
CO2 in our atmosphere keeps rising. This article by By: Hannah Ritchie and Max Roser explains the problem. See the chart below which spells out the seriousness of the situation. In short, we need a rapid programme:
- Moving power generation industry to renewable energy
- Ending fossil fuel exploitation
- Moving transportation (cars & road transport) away from the use of petrol and diesel engines
- Designing buildings and homes for zero emissions, including getting rid of gas boilers.
The ‘how’ is largely up to the Government and the willingness of people to change.
I hope this explainer has been useful.